Lauric Acid
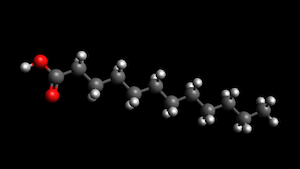
The lipid shown here is Lauric Acid in a ball-and-stick configuration.
Lauric Acid is a saturated fatty acid.
Lauric Acid - CH3(CH2)10COOH - (C:D = 12:0)
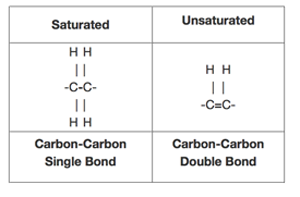
The structure of saturated and unsaturated chemical bonds looks like the diagram below.
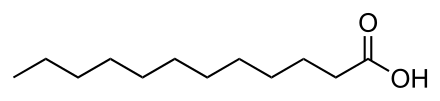
Saturated fatty acids are of the form R-COOH
Lauric Acid and Health
Lauric acid increases total serum cholesterol more than many other fatty acids, but most of the increase is attributable to an increase in high-density lipoprotein (HDL) (the "good" blood cholesterol). As a result, lauric acid has been characterized as having "a more favorable effect on total HDL cholesterol than any other fatty acid [examined], either saturated or unsaturated".[See: Mensink, RP., et.al., Effects of dietary fatty acids and carbohydrates on the ratio of serum total to HDL cholesterol and on serum lipids and apolipoproteins]. In general, a lower total/HDL serum cholesterol ratio correlates with a decrease in atherosclerotic risk. Nonetheless, an extensive meta-analysis on foods affecting the total LDL /serum cholesterol ratio found in 2003 that the net effects of lauric acid on coronary artery disease outcomes remained uncertain. A 2016 review of coconut oil (which is nearly half lauric acid) was similarly inconclusive about the effects on cardiovascular disease risk.
Foods with Lauric Acid
Coconut oil is roughly half lauric acid, so it has about 6.5 grams per tablespoon.Lauric acid makes up just under 3 percent of the total fat in cow's milk and just over 3 percent of the fat in goat's milk.
Fats in Cooking and Health
- What are the differrent types of fatty acids?
- What are Trans Fats?
- What is the difference between LDL and HDL?
- What are the different types of omega 3 fatty acid?
- What are omega-6 fatty acids?
- The importance of the ratio of omega-6/omega-3 essential fatty acids
- What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated fats?
- What causes oils to go rancid?
- What are essential fatty acids?
- Duck Fat as an alternative to butter
- How to render duck fat
- Did butter get a bad rap?
Types of Fatty Acids
Saturated